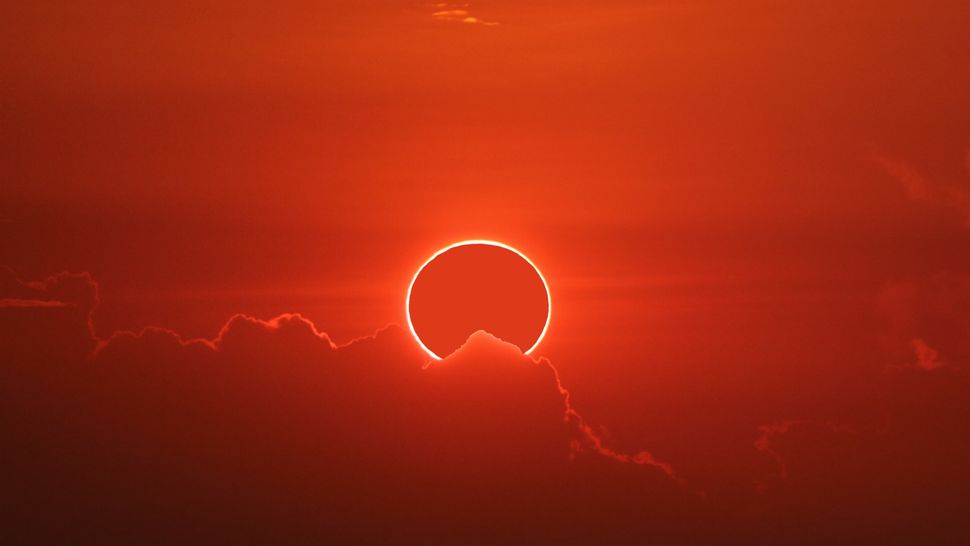



A new celestial event, a "ring of fire" annular solar eclipse, will be visible from South America and parts of Hawaii and the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans on October 2, 2024. This phenomenon occurs when the moon moves between the Earth and the sun, creating a ring-shaped silhouette of sunlight. Skywatchers are advised to use proper eye protection to view the eclipse safely.
The "Ring of Fire" Solar Eclipse of 2024
A celestial spectacle of cosmic proportions is scheduled to unfold on October 2, 2024, with the occurrence of an annular solar eclipse. This awe-inspiring event will be visible from South America, parts of Hawaii, and vast stretches of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
Annular Solar Eclipse: A Cosmic Ring
An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes directly between the Earth and the sun. However, instead of completely blocking the sunlight, the moon's apparent size is smaller than the sun's, creating a mesmerizing ring of light around the dark silhouette of the moon. This phenomenon is often referred to as a "ring of fire" due to its striking visual resemblance.
Path of the 2024 Eclipse
The path of the annular solar eclipse of 2024 will begin in the eastern Pacific Ocean, close to the coast of Chile. It will sweep across South America, passing over Argentina, Uruguay, Brazil, and Chile before exiting the continent. Observers in parts of Hawaii, including Mauna Kea, will also be treated to a view of this celestial event.
Eye Protection Crucial
It is crucial to emphasize that observing a solar eclipse without proper eye protection can lead to permanent eye damage. Skywatchers are strongly advised to wear certified solar eclipse glasses or use solar filters specifically designed for this purpose.
Top 5 FAQs on Solar Eclipses
Q1: Why does a solar eclipse occur? A: A solar eclipse occurs when the moon aligns directly between the Earth and the sun, blocking out the sunlight.
Q2: What is the difference between a total and an annular solar eclipse? A: In a total solar eclipse, the moon completely blocks out the sun, while in an annular eclipse, the moon is smaller than the sun, resulting in a ring of sunlight around the moon's silhouette.
Q3: How often do solar eclipses occur? A: Solar eclipses occur relatively frequently, but they are only visible from certain locations on Earth.
Q4: Are solar eclipses dangerous to view? A: Viewing a solar eclipse without proper eye protection can cause severe and permanent eye damage.
Q5: When was the last annular solar eclipse? A: The last annular solar eclipse occurred on June 10, 2021, and was visible from parts of Europe, Africa, and Asia.
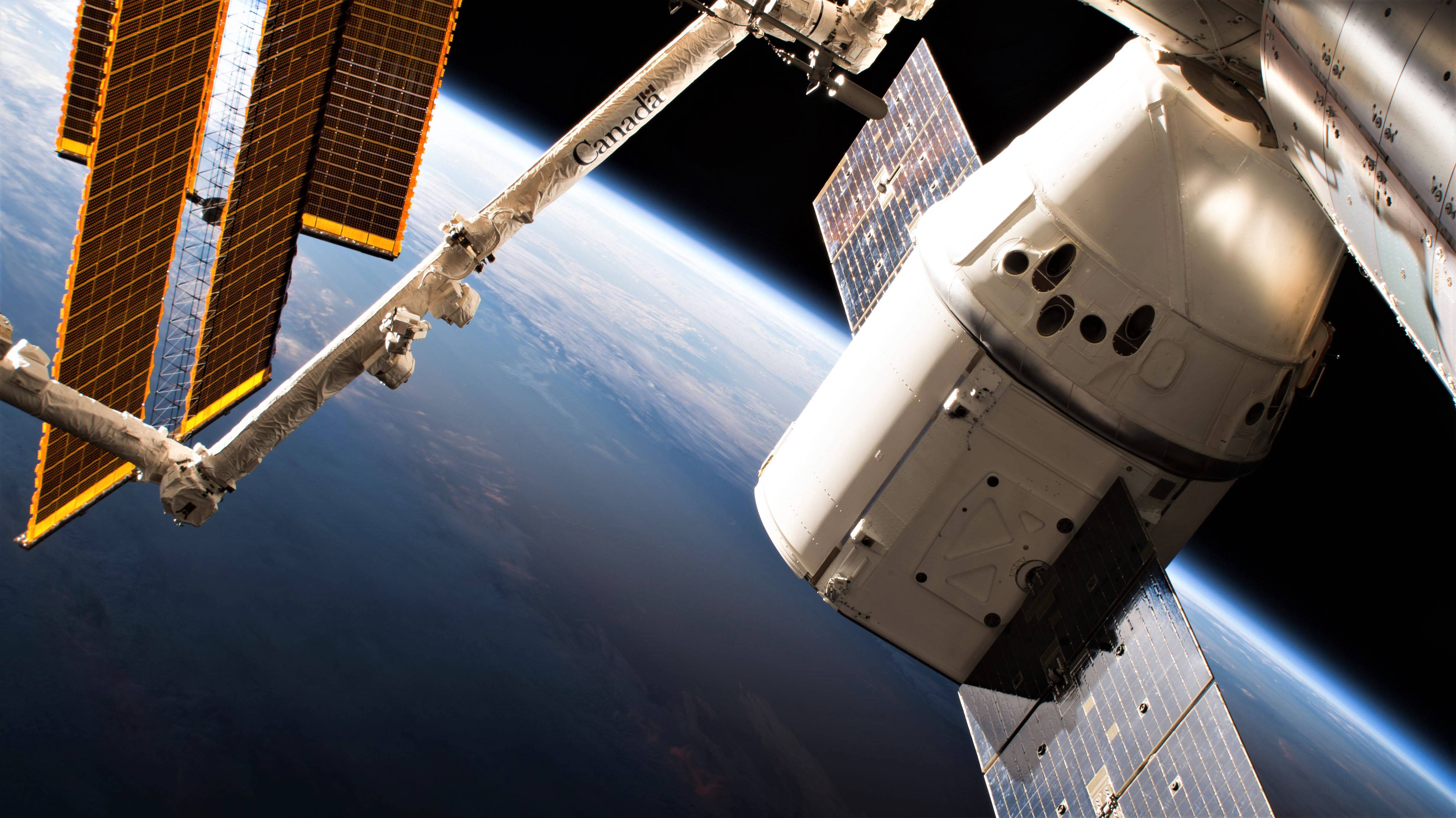

In a dramatic return, a SpaceX Dragon capsule splashed down off the coast of Oceanside last night, carrying 6,700 pounds of equipment and cargo from the International Space Station. Among the items returning to earth were materials that were exposed to space to study the effects of ultraviolet radiation, and 5 books used in NASA's Story Time from Space project. These STEM-related books were read and experimented upon by crew members aboard the space station for the educational project.

World Multiple Sclerosis Day is observed every year on May 30 to raise awareness about the condition, which affects over 1.8 million people globally. While there is no cure for MS, there are ways to manage its symptoms. Here are some tips from Johns Hopkins Medicine, including the importance of diet and exercise, creating a safe and efficient living space, and connecting with support groups. Disclaimer: Always consult a medical professional before making changes to your lifestyle.
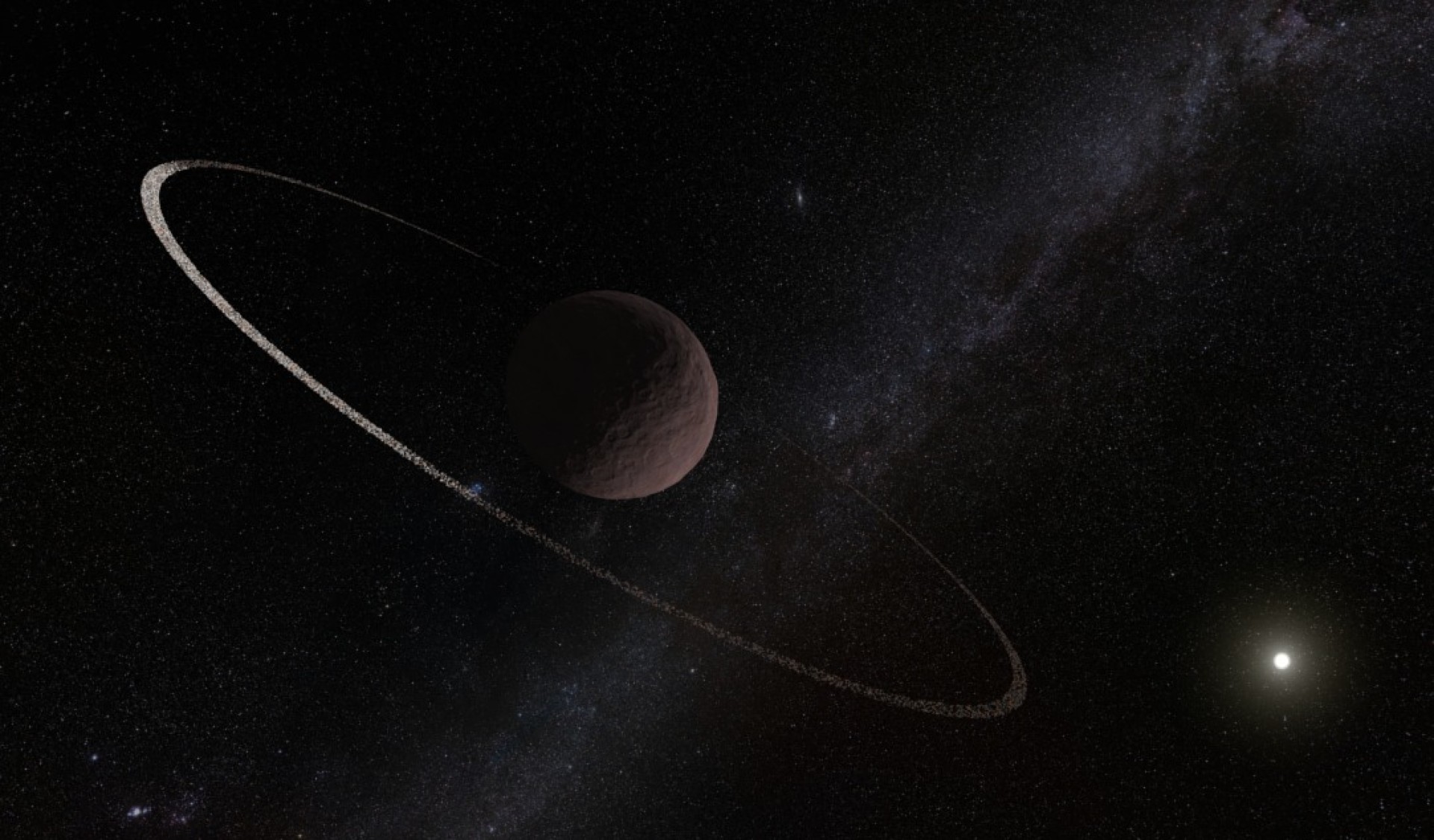

A team of astronomers led by Sihao Cheng has discovered a new dwarf planet, 2017 OF201, beyond the orbit of Pluto. The distant object has an orbital path that takes it 25,000 Earth-years to complete one revolution around the sun. Its discovery may provide insights into the mysterious "Planet 9" and its effect on objects in the outer solar system.
The ancient science of Ayurveda is gaining global recognition as a powerful ally in the quest for sustainable health. At Himalaya Wellness Company, their approach combines traditional wisdom with cutting-edge scientific validation and advanced technology. This convergence is driving the resurgence of Ayurveda and is expected to reach a market size of USD 26.26 billion by 2032. With the World Health Organization's recent validation and digital innovation opening access to previously untapped markets, the future of healthcare is being transformed by this ancient knowledge meeting modern science and technology.

A new report from Climate Central has shown a concerning increase in extreme heat in Kansas, leading to an average of 25 pregnancy heat-risk days annually. This poses serious risks for pregnant women, from preterm birth and pregnancy loss to gestational diabetes. Doctors are urging pregnant women to take precautions and listen to their bodies, including staying cool and hydrated, and being aware of any National Weather Service heat advisories in effect.

India's young cricket sensation, Shubman Gill, has been named the captain of the country's Test team in what is seen as a move towards the future. Gill, who hails from a small village in Punjab, has been widely touted as the next big thing in Indian cricket with his consistent performances and calm demeanor. At just 25 years of age, he has the responsibility of leading India in the longest format of the game, and will no doubt be looking to emulate the success of his predecessor Virat Kohli.
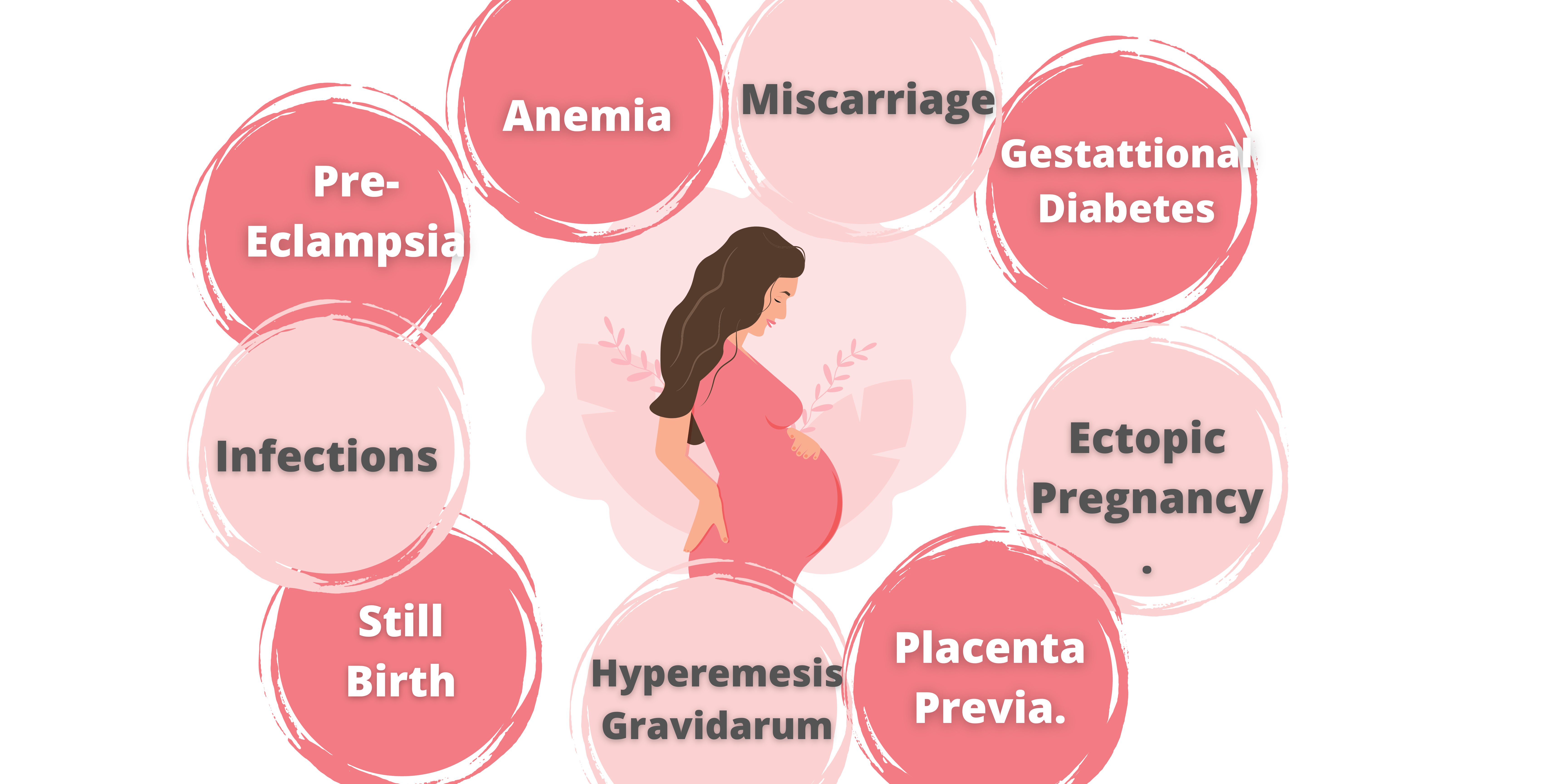
Pregnancy is a joyous time, but it can also bring about unexpected medical complications that can affect both the mother and baby. Some of the most common complications include gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, preterm labor, placenta previa, and miscarriage. Fortunately, with early detection and proper treatment, most of these complications can be managed and even prevented to ensure a healthier and safer pregnancy. Regular prenatal check-ups, proper knowledge and awareness, and prompt reporting of any abnormal symptoms are crucial in promoting better outcomes for both the mother and baby.
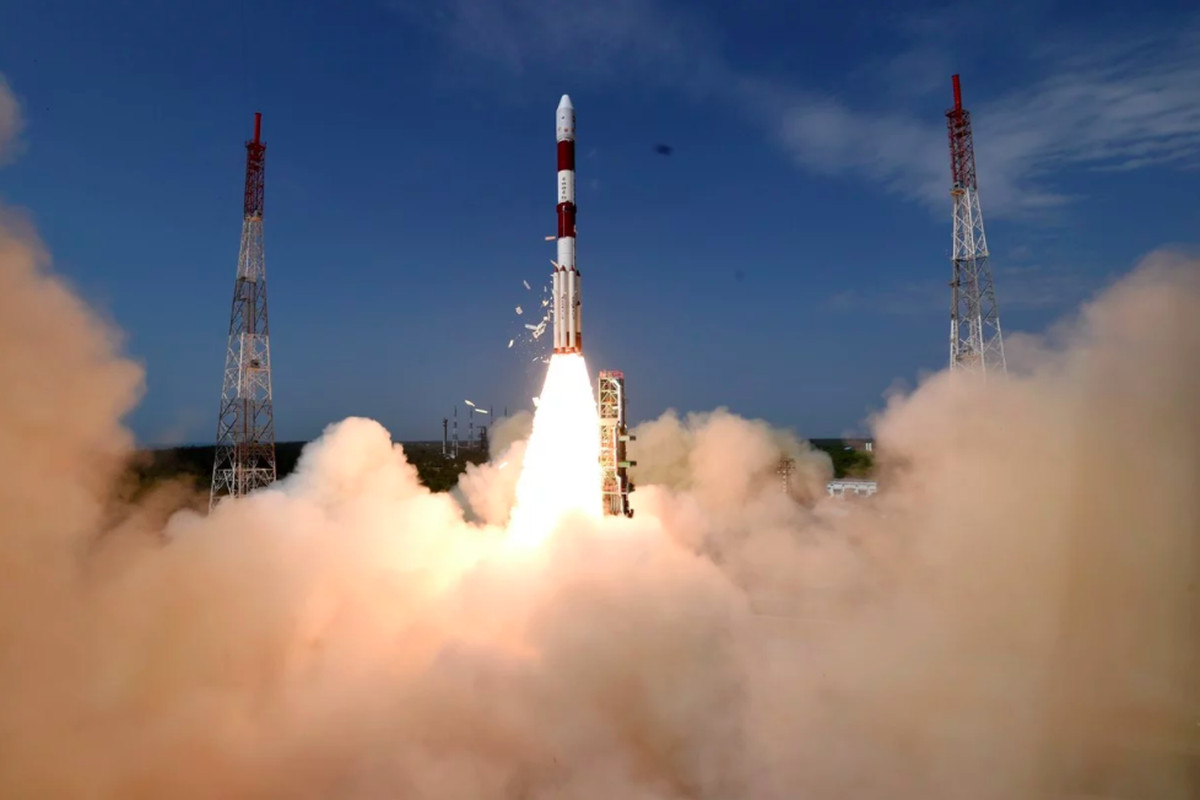

In a rare failure for India's space agency ISRO, their main rocket PSLV encountered problems during its 101st mission. The third stage of the PSLV rocket, which was the most successful launch vehicle for ISRO, experienced issues and couldn't place the earth observation satellite into the orbit as planned. This serves as a reminder of the complexities and risks involved in spaceflight, even for proven vehicles like PSLV.
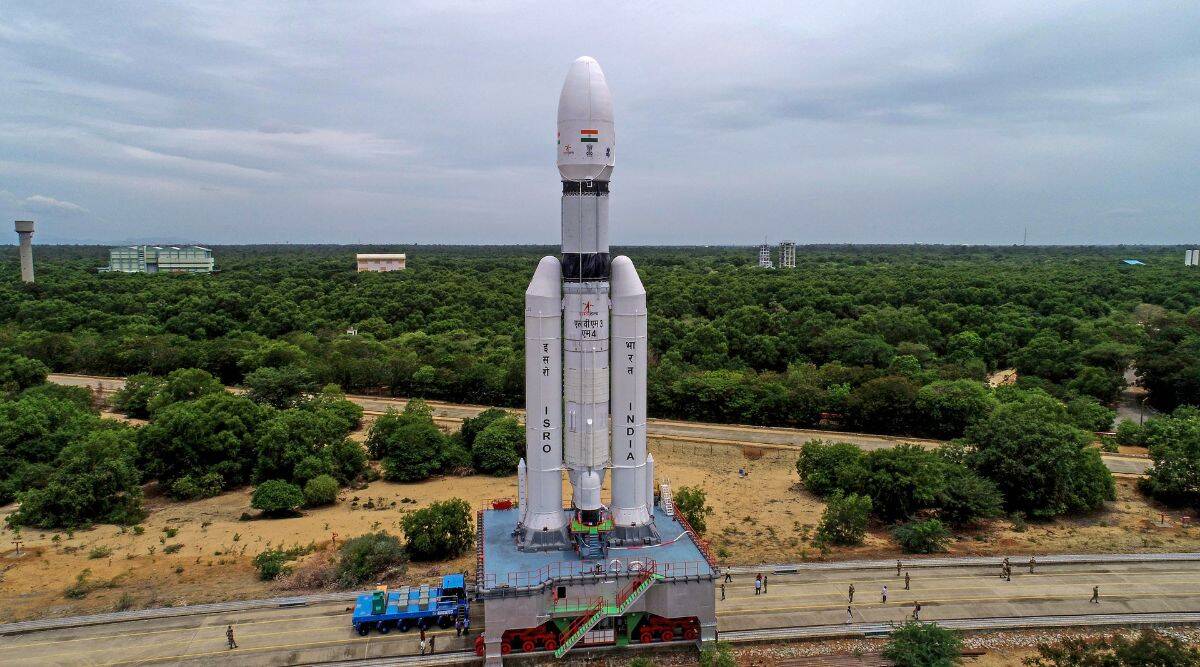

ISRO's mission to launch an Earth observation satellite aboard the PSLV rocket was unsuccessful on Sunday due to a problem in the third stage of the launch vehicle. Despite initial success in the first and second stages, a drop in chamber pressure prevented the mission from being completed. ISRO plans to regroup and attempt the mission again in the future, with the goal of ensuring a debris-free launch. This mission aimed to provide essential remote sensing data for various applications, including disaster management and national security.

A new high-altitude atmospheric monitoring station has been established in Udhampur, Jammu and Kashmir, to better understand the formation of ice crystals in clouds and their impact on rainfall. This cutting-edge facility will be the first in India to enable the study of ice nucleating particles (INPs), the rare and hard-to-detect tiny particles that are the starting points for the formation of ice crystals in clouds. By bridging this critical information gap, scientists hope to improve their ability to model cloud behavior and make more accurate precipitation predictions, especially for extreme events. The new center, which is located at 2,250 meters above sea level, was inaugurated last week and will collaborate with Swiss scientists from ETH Zurich to conduct INP studies. This facility will offer unique insights and contribute to our understanding of precipitation processes worldwide.